
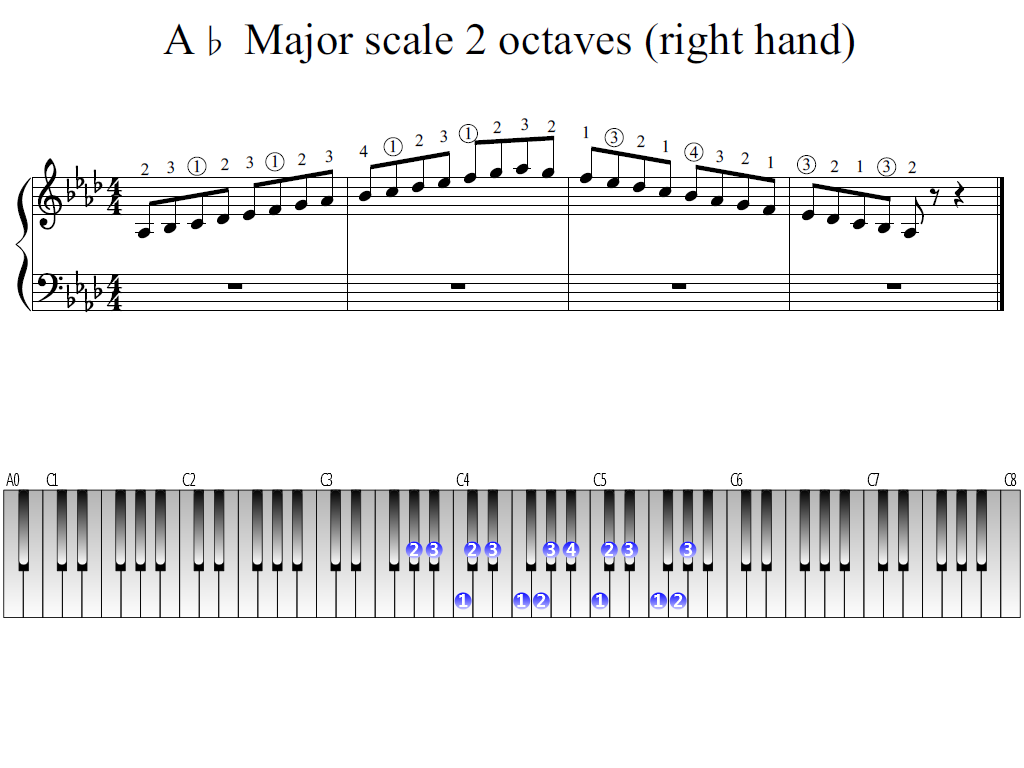
Your browser does not support the audio element. The diagrams below show the order of intervals in the major and minor modes: On the sixth degree of each major scale you can start a minor scale (called the relative natural minor) that uses the same sounds. Each diatonic scale has seven degrees before reaching its octave. The first note of the scale is called the first degree. A scale that employs the minor mode starting on G is called G minor. So, for example, a scale that employs the major mode starting on F is called F major. Scales are named according to the note on which they begin and their mode. In classical music there are two modes: major and minor. The different patterns of tones and semitones in which we climb the diatonic scales are known as modes. Most commonly used are the diatonic scales - formed from seven sounds that divide the octave into five tones and two semitones arranged in various ways, and never with two consecutive semitones.

We can go up two steps at a time and we will have a whole-tone scale (scale composed tone intervals), or we can go up using a mixture of tones and semitones. We can play all the steps and, in this case, we will obtain a chromatic scale (a scale composed by semitone intervals). There are several ways to "go up" or "down" a scale. The difference between one pitch and its nearest neighbour is called a semitone. The scale should be understood as a series of steps, and for this we have to imagine the piano keyboard as a series of equally spaced pitches. The term scale indicates a series of sounds sorted in ascending or descending order of pitch, starting from any note and continuing until it reaches the octave above or below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
